
Organizations can achieve sustainable competitive advantage and long-term stability through well-functioning supply chains. In order to maintain a successful and efficient supply chain, it is necessary for organizations to develop strong partnerships with all suppliers in their ecosystem. A supply chain partnership is a collaborative relationship between two or more organizations that share capacities and capabilities to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of their ecosystem. There are many benefits of supply chain partnerships, such as improved flexibility, traceability and predictability. In addition, partnerships can also lead to increased resilience. As per recent observations of Gartner in its “Hype Cycle for Supply Chain Strategy, 2022”, it is estimated that the businesses in next 5 to 10 years will be able to proactively mitigate risks to ensure business continuity. To achieve this resiliency and be adaptable to the evolving BANI (Brittles, Anxious, Non-linear, and Incomprehensive) world, the businesses need to establish matured ecosystem partnerships over the next 2-3 years.
However, forming and maintaining a long-term strategic partnership can be challenging. In order to create and maintain a successful partnership, it is important to understand the different building blocks of a supply chain partnership model. The parties involved must determine and agree on possible motivators, contributing factors, business process components and expected results, taking into account the balance of power, specialization, readiness for cooperation of stakeholders, possible damage and distribution of risks and more. Building on the existing partnership model by Douglas M. Lambert and A. Michael Knemeyer, our RACE model is developed to help food businesses and supply chain leaders understand the different building blocks of a supply chain partnership model.
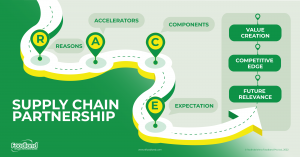
R – Reasons
Partnership reasons are the prime drivers for which the partners should consider getting into a partnership. Outsourcing or delegating non-core activities or processes helps businesses concentrate resources & expertise in the area of their own competence. Resulting into significant competitive advantages through the desired drivers. As per HBR’s latest report, resiliency is the prime reason that drives supply chain leaders to form supply chain partnerships. Identification of reasons should be accompanied by awareness of the asset-cost effectiveness. Here businesses need to identify and build a specific description for each category with metrics and targets. E.g.: Improving utilization from 80% to 98% or cutting product costs by 7% per year.
Reasons for partnering can be listed under these major categories:
- Asset and cost efficiency
- Customer service
- Marketing advantage
- Profit stability/growth
Partners should openly discuss possible disputable points and motives, justifying the target values of their expectations.
A – Accelerators
Accelerators are contributing factors that influence and facilitate implementation of a strategic supply chain partnership. Here the representatives of the parties jointly consider the organizational environment in which the partnership will be built. Various factors such as compatibility of corporate cultures and management methods and more are evaluated. It takes a lot of effort to conduct a thorough and accurate assessment of these factors, but it is worth it.
Accelerators need to be evaluated to check compatibility:
- Compatibility of corporate cultures, management philosophy & techniques,
- Strong sense of mutuality,
- Symmetry between two parties (comparable scale, industry position, and brand image)
- Presence of common competitors and consumers,
- Congruence of companies,
- Advantageous locations; exclusive conditions,
- Previous experience of cooperation.
The better the assessment of accelerators – the more convincing the intentions in favour of partnership and cooperation.
C – Components
Components form the structure of the partnership model with regard to the plan and control of joint economic activities of involved parties with adequate distribution of risks and rewards. Evaluating the components of a supply chain partnership model is important for a number of reasons. First, it helps identify potential bottlenecks or inefficiencies in the supply chain, which can then be addressed to improve the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the supply chain. Second, evaluating the components of a supply chain partnership model can help identify areas for improvement and potential opportunities for cost savings. Third, regular evaluation can help ensure that the supply chain is meeting the needs of the business and its customers, and that it is aligned with the overall goals and objectives of the organization.
Components to evaluate:
- Capability for planning (Planning style, level, content)
- Joint operations control (Measurement, ability to make changes)
- Communication (Non routine, day-to-day)
- Risk/reward sharing (Loss tolerance, gain commitment, Commitment to fairness)
Based on partners’ outcome expectations the components need to be adjusted.
E – Expectations
Partnerships are justified only if they stand to yield substantially better results than the firms could achieve on their own. As per GEP’s findings, businesses have realised 20% reduction in lead times and inventory related costs, coupled with productivity improvement. And even if they are warranted, they can fail if the partners enter them with mismatched expectations. Thus, it is important for both partners to mutually discuss and set expectations at the start to avoid discrepancies at later stage. The model offers a process for aligning expectations and determining the most productive level of partnering. It helps establish mutual understanding and commitment required for success and provides a structure for measuring outcomes.
Partnership with the right expectations can help achieve the following outcomes:
- Focus on core competencies
- Improved product quality
- Reduced costs
- Sustainable competitive advantage
- Assured future-relevance
- Enhanced value creation
- Resilience in uncertain situations
Partnerships, however, are costly in terms of the time and effort required. Consequently, a business cannot and should not partner with every supplier, customer or third-party provider. It is important to ensure that adequate resources are dedicated to the relationships which will truly benefit from a partnership. The partnership model provides a structured process to effectively and efficiently build and maintain tailored business relationships that may become an asset for a business looking for competitive advantage.
To build a strong partnership foundation using RACE model, connect with our experts.








